
Fast, affordable Internet access for all.

Knoxville, Tennessee's Knoxville Utility Board (KUB) says it has completed the first phase of its ambitious broadband deployment, bringing affordable fiber access to more than 50,000 premises in this city of 192,000 – many for the very first time.
When we last wrote about KUB back in 2021, the city's utility had just received approval to build what will eventually be the biggest municipal broadband network in the U.S.
All told, the $702 million project, known as KUB Fiber, aims to deliver affordable fiber to 210,000 households across KUB’s 688-square-mile service area, taking between seven and ten years to complete.
KUB says that the first phase of fiber deployment involved the installation of more than 1,100 miles of fiber infrastructure. Upgraded users have the option of three tiers of service: symmetrical gigabit per second (Gbps) service for $65 a month; symmetrical 2.5 Gbps service for $150 a month; and symmetrical 10 Gbps service for $300 a month.
KUB’s service tiers do not come with usage caps or long-term contracts. Unlike many municipal operations, KUB is also offering locals the option of bundling television service.
KUB was driven to expand access after more than a decade of local frustration at the slow speeds, high prices, and spotty coverage caused by a notable lack of competition between regional telecom monopolies, AT&T and Comcast (Xfinity). Both companies have attempted to lock down customers via long-term contracts ahead of the network’s completion.
As one local resident said:
“Comcast thanked me for being a customer for 23 years, but it's not because I've had the option to go anywhere else. They have had 23 years to fix these problems and they haven't."
A plan in Jamestown, New York to deploy affordable fiber to every last city resident has received welcome support from state leaders, even though deployment details remain murky and network construction remains well over the horizon.
In 2021, Jamestown officials told ILSR they were working with Entrypoint Networks on a $25 million fiber network for the city of 28,000. The city hopes to deliver fiber in conjunction with the Jamestown Board of Public Utilities, leaning heavily on the federal Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP) to ensure low cost access to marginalized and low income communities.

The city’s plans got a needed attention boost last month when Empire State Development – tasked with boosting economic development across New York State – gave a nod to Jamestown’s efforts in the organization’s five-year development plan.
The plan, among other things, will shape how the state utilizes $664 million in federal subsidies made possible by the Broadband Equity Access and Deployment (BEAD) Program and the 2021 infrastructure bill. While Jamestown may qualify for BEAD funding, how much the city’s project could receive remains undetermined.
Both the Sagamore Bridge and Railroad Bridge that span opposite ends of the Cape Cod Canal carry the kind of traffic that terrifies Comcast and Verizon.
The 576 count fiber-optic strand strung across the Railroad Bridge in Buzzards Bay – and the 864 strand that crosses the Sagamore Bridge – belongs to OpenCape, an open-access “middle mile” network ushering the gold-standard of Internet connectivity into parts of each of the Cape’s 15 towns.
It’s an extension of OpenCape’s fiber network, lashed to utility poles in dozens of communities across southeastern Massachusetts, all of which connect the region to the nation’s Internet backbone/long haul network.
Middle mile networks are a key part of the Internet’s connective tissue that dramatically lowers the cost for Internet service providers (ISPs) to deploy “last mile” connections to individual homes and businesses.
Thanks to a federal grant courtesy of the American Recovery and ReInvestment Act, the nonprofit fiber network was established in 2009 and since then has been providing Internet connectivity to most of the region’s anchor institutions – hospitals, public safety facilities, numerous libraries, schools, banks, and dozens of other enterprise clients with big data needs such as the Marine Biological Laboratory and the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution in Falmouth.
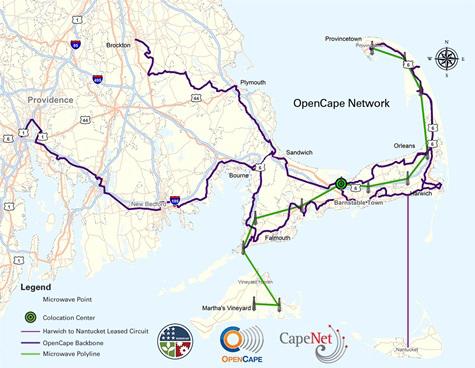
Over the past several years OpenCape has deployed fiber deeper into the region, expanding the network from an initial 350 miles to 650 miles of fiber today, serving a growing number of Main Street businesses across the Cape.
Blue River, Colorado (est. pop. 882) is the latest Colorado municipality to explore building its own broadband network with an eye on affordable access. The town is part of a trend that’s only accelerated since the state eliminated industry-backed state level protections restricting community-owned broadband networks.
Just south of Breckenridge in the central part of the state, Blue River is nestled in one of the more rural parts of Summit County. Comcast (Xfinity) enjoys a broadband monopoly, resulting in spotty access, slow speeds, and high prices. Locals also routinely complain that cell phone service remains spotty in much of the mountainous area.
In response, town leaders recently hired the consulting firm, NEO Connect, to explore the possibility of building a town-wide fiber network. According to a feasibility study presented to the Blue River Board of Trustees by Mayor Toby Babich, the construction of a fiber network serving every town resident will cost somewhere in the neighborhood of $13 million.

While that “may seem out of reach,” Babich recently told the board, “we believe with the right funding and partnership we can move forward with this project.”
The estimates for network construction range somewhere between $7 million to $24 million, depending on how much underground trenching work is required.

This week on the podcast, Christopher speaks with Deb Socia, President and CEO, and Geoff Millener, Chief Operating Officer, of the Enterprise Center in Chattanooga, Tennessee. The Enterprise Center is a non-profit partner to the City of Chattanooga that unites people, organizations, and technology to build an advanced and inclusive future.
The group discusses the HCS ED Connect program, a transformative initiative providing free home Internet access to low-income students in Chattanooga, and its notable impact on parent engagement and student success.
Deb and Jeff also shed light on the Orchard Knob project, leveraging technology to better health outcomes in African-American neighborhoods, and the Tech Goes Home program, offering technology access and training for seniors and their underserved populations.
Throughout the conversation, the group underscores the vital role of partnerships and community engagement in successfully implementing these initiatives. They conclude by emphasizing the overarching need for universal broadband access as a driving force behind fostering positive change in communities.
This show is 38 minutes long and can be played on this page or via Apple Podcasts or the tool of your choice using this feed.
Transcript below.
We want your feedback and suggestions for the show-please e-mail us or leave a comment below.
Listen to other episodes or view all episodes in our index. See other podcasts from the Institute for Local Self-Reliance.
Thanks to Arne Huseby for the music. The song is Warm Duck Shuffle and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (3.0) license.
Pikeville, Kentucky (pop. 7,300) sits about 150 miles southeast of Lexington, in the extreme eastern part of the state. Today, after almost a decade of fighting with Internet Service Provider (ISP) Optimum about service so consistently poor that the city finally sued the provider, it’s working on an alternative: a partnership that will see the local government build new citywide fiber infrastructure and lease it to an operating partner.
A Tale As Old As Time
Publicly available data shows that, historically, about two-thirds of the city of Pikeville can take Internet service from Inter Mountain Cable - a regional provider with about 25,000 subscribers across Kentucky, West Virginia, and Virginia. Likewise, Optimum (formerly Suddenlink) offers cable service to about the same number of households. AT&T’s DSL service covers a little more than a quarter of town. Those living in the northern half of the city generally have better service options than those living in the southern half.
The path the city of Pikeville has taken began almost 15 years ago. In 2009, the local government signed a new, 10-year franchise agreement with Suddenlink. But when Altice (originally a French telecommunications company) bought Suddenlink back in 2015 to build its portfolio here in the United States, things quickly took a turn for the worse.
As Loveland, Colorado’s municipal broadband network continues to rack up industry accolades on its path to providing world-class high-speed Internet service, the city is now celebrating another important milestone.
Last week, Pulse Fiber officials announced that construction of its community-owned broadband network is now complete with every household and business in this city of 77,000 now having access to affordable gig-speed service.
The $110 million construction project, which began in earnest only four years ago, is the largest capital project in the city’s history, reaching the finish line on time and on budget, city officials said.
In a press announcement Steve Adams, Loveland’s City Manager, captured the meaning of the moment:
“As we celebrate the successful conclusion of this historic project, Pulse stands as a shining example of what is possible when the community unites to pioneer innovative, collaborative solutions. We did this for ourselves, and we made it happen together.”
“This infrastructure has been designed and built with future generations in mind, ensuring Loveland remains at the forefront of modern, robust, and future-proof Internet delivery,” Pulse Broadband Manager Brieana Reed-Harmel added.

Pulse officials candidly acknowledged that the pathway to the leading edge of Internet connectivity wasn’t easy, as the city had to navigate network construction through a global pandemic, supply chain disruptions, and inflation. But despite those challenges, Pulse Fiber has deployed 631 miles of conduit and over 1,300 miles of fiber throughout the city.
CVFiber continues to make progress in deploying affordable fiber to long-neglected rural areas in Vermont, as the state’s effort to embrace CUDs (Communications Union Districts) as a cornerstone of bridging the digital divide also pays dividends.
In late 2022 CVFiber broke ground on an ambitious plan to build a 1,200-mile fiber-optic network to bring affordable gigabit broadband access to 6,000 rural Vermont addresses deemed underserved by commercial broadband providers.
According to an October announcement by the CUD, its first customers have been connected in the central Vermont town of Calais, with construction ongoing in nearby Middlesex, East Montpelier, and Worcester.

“We are enthusiastic about our progress as we bring high-speed Internet to central Vermont communities,” CVFiber Executive Director Jennille Smith said. “The progress that we have made and the impact that we’ve been able to achieve to date could not have been accomplished without the unwavering commitment from our partners. We are optimistic as we expand to other service areas.”
CUDs have proven to be a useful way for municipalities to band together to cooperatively build broadband projects that may have been financially and logistically impossible to try alone. Vermont CUDs can legally fund needed broadband expansions through debt, grants, and donations—but not taxes, though they themselves are tax-exempt nonprofits.
CVFiber’s fiber deployment is expected to cost $60 million, $27 million of which is being paid for by federal grants made possible by the American Rescue Plan Act (ARPA). The remaining cost is expected to be funded by network revenue, loans, and future grant opportunities.
New England residents have been complaining about Verizon’s lack of meaningful fiber upgrades for the better part of the last two decades, prompting a steady parade of interest in community owned and operated fiber networks in states like Massachusetts.
But some of these community broadband efforts, such as West Springfield’s plan to deliver affordable fiber access to every city resident, are still being hampered by Verizon.
In 2021 the city (est. pop. 28,000) announced it would be partnering with Westfield Gas and Electric, the publicly owned utility in Westfield, Massachusetts, which has built and operates fiber networks in nearly two dozen communities in the Berkshires. The end result: Westfield Gas and Electric's broadband subsidiary Whip City Fiber plans to deliver West Springfield residents symmetrical gigabit fiber for $75 a month, without long term contracts or onerous hidden fees.
But efforts to launch a $1.8 million pilot project have been on hold thanks to ongoing delays by Verizon and Eversource to prepare local utility poles for fiber attachment, West Springfield Chief Technology Officer Stephanie Straitiff tells local news outlet The Reminder.
Lancaster, Pennsylvania has revitalized the city’s long percolating plan for a municipal broadband network, this time via a public-private partnership (PPP) with Shenandoah Telecommunications Company (Shentel). The city’s quest for more affordable, reliable broadband is a quest that’s taken the better part of a decade to finally come to fruition.
Lancaster city officials recently announced that they’d selected Shentel with an eye on ensuring uniform broadband availability to the city of 57,000.
“In 2022, the City issued an RFP for a partner to achieve stated goals, which received five responses, and led to the selection of Shentel,” the city said. “The contract will result in Shentel installing fiber at its sole cost to provide service to 100% of the city’s residents. Shentel plans to commence design and construction immediately upon execution of the final agreement.”
According to Lancaster officials, the city hired CTC Technology & Energy Engineering & Business Consulting to evaluate the city’s needs. The determination to proceed with a PPP with Shental was driven, in part, by the historic broadband grant opportunities being created thanks to the 2021 Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA), and the American Rescue Plan Act, the latter of which provided $39.5 million to the city.