Image


Fiber to the Home
Tuesday's ceremony was the kickoff to the construction phase of a huge, multi-agency, multimillion-dollar project to deliver that broadband access to 2,500 homes and businesses and 137 community buildings. The agencies, the cities of Champaign and Urbana and the University of Illinois, were notified 18 months ago that they were to be the recipients of a $22.5 million federal stimulus grant to build the Internet infrastructure. That was paired with a $3 million grant from the state of Illinois and hundreds of thousands dollars more from the local agencies. After spending the intervening months planning the network, officials gathered in Douglass Park on Tuesday with shovels and hard hats in hand. Construction crews will be burying 278 miles' worth of fiber throughout Champaign-Urbana during the next months, and organizers hope to be delivering Internet and cable service to eligible businesses and homes within the next year.
 The goal is ultimately to connect everyone -- residents and businesses -- with the best network possible, allowing independent ISPs to offer services. However, this approach is somewhat new, with a lot of diverse stakeholders trying to work together so it will undoubtedly be a project to watch and learn from.
Follow the project and learn more about it on their site.
The goal is ultimately to connect everyone -- residents and businesses -- with the best network possible, allowing independent ISPs to offer services. However, this approach is somewhat new, with a lot of diverse stakeholders trying to work together so it will undoubtedly be a project to watch and learn from.
Follow the project and learn more about it on their site.The city will order 5,000 additional set-top boxes for Fibrant at the discounted price of $721,572… Fibrant’s original inventory of 5,000 set-top boxes purchased in March 2010 is running low, Behmer said. The city’s new broadband utility, which sells Internet, cable TV and phone services to Salisbury residents, has about 1,200 customers and averages about three set-top boxes per home, he said.This is a reminder of the economics of these networks. Each set-top box costs something like $150. Household that subscribes for television service average 3 set-stop boxes, meaning that the cost of those boxes alone is about $450 of loss to Fibrant before the subscriber pays a dime to Fibrant. This is why muni networks take so long to break even. The additional install costs like the equipment on the side of the house and the labor to set everything up grow quickly -- often to between $1200-$1500 per subscriber. It takes years to pay down those costs, plus the interest of borrowing to build the network. So when you hear that a community network is running in the red in year 3, you should say, "Duh." Infrastructure often takes a long time to pay off, which is one of the main reasons the private sector does such a poor job of providing it.
Redwood County’s Economic Development Authority (EDA) opted to move forward with a broadband feasibility study that would determine just what the county would need to do in order to get fiber to every premises. … The study, which is being conducted by the Blandin Foundation through what is known as the Robust Broad-band Networks Feasibility Grant Program. The grant, which includes up to $40,000 for the county as it addresses the needs of every community and farm site from one end of the county to the other, requires matching funds, which are available through the county EDA.
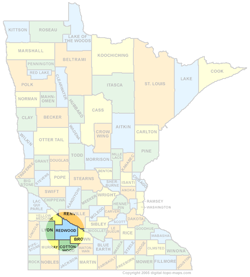 Redwood County is in an interesting area, just north of the Windom area muni FTTH networks and west of the proposed project in Sibley and Renville counties. This study comes not long after Todd County started a feasibility study as well (the the latest on that). And though we haven't discussed it much on MuniNetworks.org, Lac qui Parle County to the northwest is working with a rural telephone cooperative to bring FTTH to many in their border as well.
And then beyond them, we have Cook County going FTTH with their electric coop and Lake County going its own way, both with the assistance of the broadband stimulus awards.
Minnesota could very well become the state with the most impressive rural connections. Unfortunately, thus far we have seen no assistance from the state in this matter, but perhaps the Dayton Administration will chart a new course.
Redwood County is in an interesting area, just north of the Windom area muni FTTH networks and west of the proposed project in Sibley and Renville counties. This study comes not long after Todd County started a feasibility study as well (the the latest on that). And though we haven't discussed it much on MuniNetworks.org, Lac qui Parle County to the northwest is working with a rural telephone cooperative to bring FTTH to many in their border as well.
And then beyond them, we have Cook County going FTTH with their electric coop and Lake County going its own way, both with the assistance of the broadband stimulus awards.
Minnesota could very well become the state with the most impressive rural connections. Unfortunately, thus far we have seen no assistance from the state in this matter, but perhaps the Dayton Administration will chart a new course.SOUTH ROYALTON – Having completed its beta testing, and with the Phase I project nearly complete, ECFiber began connecting its first customers today. Eight customers have been beta-testing the system for the past two weeks, getting sustained 5Mbps symmetrical service. The Barnard General Store, one of the beta sites, has been offering the experience to customers via WI-FI, and has been finding folks on their doorstep at all hours, trying out the system.“It’s been amazing,” says Kim Furlong, one of the store’s proprietors. “Because so much more of what we do is online, it is truly a joy to reap the reward of high-speed internet. Dial-up, and even satellite, is such a time-robber. Fiber is very different – you can be more efficient, and that is exciting. At the same time, I have some trepidation. People are going to relocate here more permanently because of what is available, and that is probably going to change the fabric of the community.” According to Project Coordinator Leslie Nulty, 15 new accounts were opened within the first 24 hours after the doorstep delivery of information packets. Barnard Academy, another beta site, is also very excited about the service. They are planning an open house and community celebration of ECFiber’s arrival in mid-October. Barnard was chosen for the Phase I project because of its proximity to the central office and its large number of unserved users. Pre-registrations topped 90% before the project started. Phase II, to build out the rest of the town of Barnard, is in the planning stages, with an informational meeting set for Thursday night at 7PM at the Barnard Town Hall.

“We’d love to have it,” said Cris Hogan, executive vice president of Hogan & Associates Construction in Centerville. “It’s much faster, with more capabilities, and we’re hoping less expense.” As a commercial builder, Hogan’s company frequently transfers detailed documents and plans to subcontractors electronically. Under current bandwidth conditions, that process can be time consuming, he said. Hogan’s wait for screaming-fast Internet could soon be over. “No one in Centerville has Utopia right now but they’re getting close with the stimulus,” said Blaine Lutz, the city’s finance director. His workplace, Centerville City Hall, should be hooked up by October.The current expansion will connect 141 anchor institutions in the two communities as well as many more in Payson, Orem, Murray, Midvale, West Valley City, and Perry. As of now, residents generally have to pay a steep upfront $3,000 connection fee for the physical connection, but local governments are investigating different options to allow residents to connect to the network affordably, as Brigham City did with a special assessment area. As for the capacity of the network and value offering, it crushes Comcast.
What happens now? This is a pilot program, so we’re taking it step-by-step. We want the residents and property owners in Cascadia/Bornstedt Villages to be partners with us in making decisions on how this service will work. And we want it to be democratic: whatever we do, it will only be with the support of the majority of the residents and property owners who get involved. The first thing we need to know is: how would you like to be involved? We have a lot of options, depending on your level of interest, and how busy your life is. On one end of the spectrum is simply asking us to keep you informed through e-mail or letters, and at the other end is your active participation (over a course of several meetings) in the detailed planning for the implementation of this pilot project.
The first attempt at getting that approval didn't go so well in 2009. According to city records, opponents -- including the Colorado Cable Telecommunications Association -- spent $245,513 to defeat that ballot measure, the largest amount ever spent on a Longmont city election. By contrast, the city legally couldn't campaign on its own behalf, and the explanations that were out there didn't explain well, according to Longmont Power & Communications director Tom Roiniotis.The cable and phone companies created an astroturf group called "No Blank Check" that then used standard fear, uncertainty, and doubt tactics to spread misinformation around the community.