
Fast, affordable Internet access for all.

Fiber to the Home
Allegan County, Michigan is moving forward with an ambitious new plan to bring affordable fiber broadband to 12,000 unserved addresses across the county. The project will be in partnership with Southfield, Michigan based 123NET, made possible in large part due to more than $17.7 million in county American Rescue Plan Act funds.
“123NET has proposed a fiber to the home proposal to approximately 12,000 addresses of residents who don’t have access to 100 Mbps (Megabit per second) download fixed service,” Allegan County Broadband Project Manager Jill Dunham told ISLR.
According to the county’s website, the Allegan County broadband Internet access project first began when the county commission approved a resolution to form a Broadband Action Workgroup, which started meeting back on August 8, 2021.
The county has since constructed a four-part broadband expansion plan that promises to deliver 12,000 unserved addresses affordable fiber connectivity providing at least 100 Mbps downstream and 25 Mbps upstream, now effectively the standard in federally subsidized new broadband deployments.
According to the county, the path toward breaking ground involves ensuring Rescue Plan fund eligibility, hiring a project lead, bringing in additional project partners and other outside advisors, gathering data to ensure project goals will be met, and then putting it all together to implement plans for increased accessibility.
In an economy where inflation seems to be everywhere, Fairlawn, Ohio residents are getting a bit of welcome news.
Subscribers to FairlawnGig – Fairlawn, Ohio’s municipal broadband network – are being upgraded to new service levels as the city-owned network bumps up speeds and slashes prices to make its fiber Internet service faster, and even more affordable.
Earlier this week, FairlawnGig announced that subscribers who had been getting Fairlawn’s basic service tier of symmetrical 300 Megabits per second (Mbps) were being upgraded to symmetrical gig speed service – for the exact same price of $55/month.
FairlawnGig also announced that subscribers who had previously been getting gig speed service will see their bills drop down to $55/month instead of the $75/month they had been paying. Meanwhile, subscribers who were getting 2.5 Gigabits per second (Gbps) for $150/month will now be upgraded to a symmetrical 5 Gbps tier, and see their price drop to $100/month.
“That was always the plan from the very beginning,” the City of Fairlawn’s Public Service Director Ernie Staten told ILSR this week.
We have been striving at all times to bring the greatest speeds and to bring prices down. We have made it where we have done well enough financially to start lowering prices and providing greater speeds.
Local Businesses Threatened to Leave – Unless Better Internet Comes to Town
Fairlawn, a small city of approximately 7,500 Ohioans about 10 miles northeast of Akron, created a telecommunications utility in 2015 to bring city-wide access to high-speed Internet service after years of dealing with subpar broadband offerings from the incumbent providers.
The Hudson Clock Tower is the most recognizable landmark in the City of Hudson. The 44-foot tall Romanesque-style brick structure was gifted to the city over a hundred years ago by James Ellsworth, a millionaire who considered it a symbol that the time had come to modernize the city’s infrastructure having “watched the town he had grown up in, fall into disrepair.”
Now, this city in northeast Ohio, 15 miles north of Akron, is reviving the public-minded spirit of Ellsworth as it looks to modernize its telecommunications infrastructure through a public-private partnership that would expand the city-owned municipal fiber network, which now only serves part of the city, to reach all 22,000 residents who call Hudson home.
In mid-October the city issued a Request for Proposals in which “all models of network ownership will be considered (that) may either incorporate the (existing city-owned) Velocity Broadband network within the proposed network or may focus on the development of a network completely independent from Velocity Broadband.”
Proposals from prospective Internet service providers are due by Dec. 2.
Velocity Broadband and Then Some
Velocity Broadband was created in 2015 to primarily serve the city’s businesses. In the years since, the city-owned and operated network began offering residential service to a limited number of homes located along the network’s existing fiber path.
The Hudson Clock Tower is the most recognizable landmark in the City of Hudson. The 44-foot tall Romanesque-style brick structure was gifted to the city over a hundred years ago by James Ellsworth, a millionaire who considered it a symbol that the time had come to modernize the city’s infrastructure having “watched the town he had grown up in, fall into disrepair.”
Now, this city in northeast Ohio, 15 miles north of Akron, is reviving the public-minded spirit of Ellsworth as it looks to modernize its telecommunications infrastructure through a public-private partnership that would expand the city-owned municipal fiber network, which now only serves part of the city, to reach all 22,000 residents who call Hudson home.
In mid-October the city issued a Request for Proposals in which “all models of network ownership will be considered (that) may either incorporate the (existing city-owned) Velocity Broadband network within the proposed network or may focus on the development of a network completely independent from Velocity Broadband.”
Proposals from prospective Internet service providers are due by Dec. 2.
Velocity Broadband and Then Some
Velocity Broadband was created in 2015 to primarily serve the city’s businesses. In the years since, the city-owned and operated network began offering residential service to a limited number of homes located along the network’s existing fiber path.
Today, Velocity Broadband enjoys a 50 percent take-rate as it serves over 450 business and residential subscribers. The network generates nearly $1 million in revenue each year that covers all operating expenses and debt service, leaving the city with an annual net profit of $150,000.
Lexington, Tennessee is the latest U.S. city that will soon see the expansion of more affordable fiber thanks to the city-owned utility, Lexington Electric System (LES). LES’ recent $27.49 million state grant award will be the backbone of a new initiative that will both improve the utility’s electrical services, and deliver a long overdue dose of broadband competition to the area.
Cooperatives and utilities were huge winners in the latest round of awards from the Tennessee Emergency Broadband Fund, itself made possible by the American Rescue Plan. Of the $446.8 million in awards doled out by the state, utilities and cooperatives walked away with $204.4 million — or nearly half of all funds.
LES Lands Major Grant Funding
The second biggest grant recipient was LES, whose $27.49 million award will be used to deliver future-proof fiber to the 22,000 residents across Henderson, Decatur, Benton, Carroll and Hardin counties that already receive electricity service from the utility.

The utility’s original business plan estimated that it will take five years and roughly $42 million to deploy 2,101 miles of new fiber to about 88 percent (18,183) of its current electric customer base. It then proposed taking another five years — and an additional $1.2 million — to reach the remainder of the utility’s harder to reach service users.
More recent estimates proposed by the utility peg the full cost of the fiber deployment at somewhere between $50 million and $55 million.
Residents of East Carroll Parish are “cautiously celebrating” the decision by Louisiana’s Office of Broadband Development and Connectivity to uphold a $4 million GUMBO grant to bring fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) Internet service to over 2,500 households in one of the most poorly connected parts of the state.
As we reported last month, the grant had been challenged by the regional monopoly cable provider Sparklight after the state had awarded the grant to Conexon. The challenge, which claimed the cable company already serves 2,856 homes in the region, brought the project to a grinding halt on the same day residents were set to launch a sign-up-for-service event.
News that the challenge was rejected brought a sigh of relief to members of Delta Interfaith, a coalition of congregations and community-based organizations in the Louisiana Delta pushing for better broadband. Coalition members had formed an Internet task force during the Covid-19 crisis as families struggled to get access to reliable broadband.
The community and elected officials were elated when Conexon, an independent rural Internet provider, was intially awarded the grant in July – only to be frustrated when they learned of Sparklight’s challenge. Concerned that Sparklight (formerly known as Cable One) was simply gaming the state’s grant challenge process in an effort to stave off competition, community members initiated a letter-writing campaign to bring light to the challenge and pressure state officials to resolve the challenge as soon as possible.
Sparklight 'Failed to Carry Its Burden of Proof'
The city of Mountain Home, Idaho (pop. 14,000) is embracing open access city-run fiber as it pushes to expand affordable broadband to all city residents. Its stated goals: to boost broadband speeds and availability, while lowering prices 25 to 35 percent for all city residents.
Like so many city-owned broadband projects, city leaders say they were inspired by the success of Ammon, Idaho, which owns and operates an open access fiber network. That network has dramatically boosted competition in the city, drawing nationwide attention for both lower rates, and the ease with which locals can switch providers with the click of a mouse.
“The city is not trying to compete with the private sector,” the Mountain Home website proclaims. “The city will simply build and operate the fiber optic infrastructure. This infrastructure will then be open to any service provider that seeks to offer services in the city.”
With chipmaker Micron planning to build a new $15 billion fabrication plant in nearby Boise, city leaders hope to lure potential new employees through affordable broadband access. So they’re both deploying fiber conduit to every new development, and pushing an open access fiber network to lure additional competitors to the region.
That said, the network deployment is only just getting started.
In 2012 the residents of Siloam Springs, Arkansas voted against building their own fiber network after some misleading electioneering by the regional cable monopoly Cox Communications. A decade later and local residents are still frustrated by high prices and a lack of competition, as city leaders are still contemplating what exactly they should try to do about it.
In June, the city released a new report by Finley Engineering and CCG Consulting showing the width and depth of the city’s broadband issues. That report was formally presented at an August city meeting before the city’s recently-formed Broadband Advisory Committee.
Survey Said …
The survey showed that 11 percent of Siloam Springs residents still lack access to broadband, 77 percent of city residents want greater broadband competition, and 88 percent say they’re paying way too much for broadband service. While residents also complained about sluggish upload speeds and outages, the biggest consistent complaint was high prices.
“The number one issue that came through loud and clear in the surveys is broadband pricing – practically every resident we heard from thinks current broadband is too expensive,” the study authors noted.
Siloam Springs is heavily dominated by a duopoly of just two providers: Centurylink and Cox Communications. But even calling it a duopoly is generous; the city’s survey found that Cox enjoys a 92 percent broadband market share within city limits. The lack of competitive threat reduces any real incentive for the cable giant to lower prices or expand service.
In early August, the city of Holland, Michigan (pop. 33,000) voted to fund the construction of a citywide, open access fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) network. It’s the culmination of almost a decade of consideration, education, planning, and success, and builds on decades of work by the Holland Board of Public Works (HBPW) and city officials to build and maintain resilient essential infrastructure for its citizens. It also signals the work the community has done to listen to local residents, community anchor institutions, and the business owners in pushing for an investment that will benefit every premises equally and ensure fast, affordable Internet access is universally available for decades down the road.
In the Works
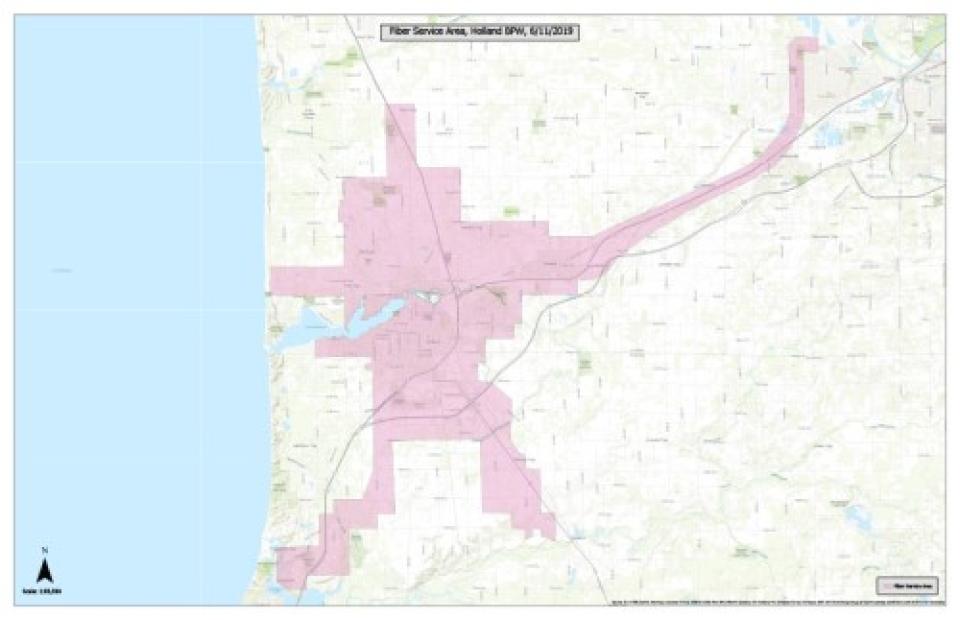
Holland has been formally exploring the need for better local connectivity since before 2016. It has been aided in this effort by the fact that the Holland Board of Public Works (HBPW), which already provides electricity, water, and waste water services, has been maintaining a small institutional fiber network that it first installed in 1992 (see current coverage in map, right, current as of May 2019).
Last March, Caribou, Maine city council members expressed unanimous support for a charter amendment allowing the Caribou Utilities District to establish a broadband infrastructure division. It was just the latest move in a multi-year quest by the city to finally deliver affordable fiber broadband access to every last city resident.
Groundwork for the effort was laid one year ago, when city council members approved using $159,000 in American Rescue Plan Act funds to craft a broadband engineering study with the help of Caribou’s Business Investment Group and executives from local ISP Pioneer Broadband.
Late last March, the Maine Senate unanimously approved LD 1949: “An Act to Amend the Caribou Utilities District Charter to Include Broadband Services,” which formally, as the name makes clear, provided approval for the CUD to expand its services into broadband access.
Now the hard work begins.
The plan as it currently stands is to build an open-access dark fiber network to every unserved Caribou residential and business location. The city would own the network, but private ISPs would provide last mile service to customers.
“We would like two or more ISPs to provide citizens with a choice of providers,” Hugh Kirkpatrick, Caribou Utilities District general manager, recently told the Bangor Daily News. “Competition should keep monthly prices lower and customer service higher.”