
Fast, affordable Internet access for all.


Ever since the Covid-19 pandemic pushed schools online, rural cooperatives and other local broadband providers have been coming up with innovative ways to connect students during this difficult time. Ozarks Electric Cooperative, with its broadband subsidiary OzarksGo, is one of the co-ops that caught our eye over the past few weeks with its creative solution.
This week, Christopher speaks with Steven Bandy, General Manager of OzarksGo, about the history of the co-op's fiber network and its new efforts to expand broadband access during the pandemic. They discuss the beginnings of Ozarks Electric's Fiber-to-the-Home network and the co-op's plan to connect all of its members in growing Arkansas and Oklahoma communities. OzarksGo has even expanded into a nearby city where it doesn't offer electric service after seeing that the community needed better quality connectivity. Co-op members are extremely enthusasitc about the co-op's fiber network, and Steven explains how people moving to the area target the Ozarks Electric service territory in their home search.
Christopher and Steven also talk about the effects of the pandemic on the co-op's fiber network, which has seen an increase in interest. Steven shares how the cooperative is partnering with a local school district to connect Wi-Fi hotspots on busses and in community buildings with fiber optic backhaul. In addition to bringing broadband access to students in response to Covid-19, OzarksGo has also increased speeds at no cost to subscribers.
This show is 19 minutes long and can be played on this page or via Apple Podcasts or the tool of your choice using this feed.
Transcript below.
We want your feedback and suggestions for the show-please e-mail us or leave a comment below.
Listen to other episodes here or view all episodes in our index. See other podcasts from the Institute for Local Self-Reliance here.
Thanks to Arne Huseby for the music. The song is Warm Duck Shuffle and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (3.0) license.

Contrary to the common narrative of poor connectivity and dim prospects for rural America, the vast majority of rural North Dakotans have gigabit fiber Internet access available to them today.
Our case study, How Local Providers Built the Nation’s Best Internet Access in Rural North Dakota, explains how this came to be, highlighting how 15 telephone cooperatives and local companies came together to invest in their rural communities and build fiber broadband networks across the state. In the 1990s, those companies united to purchase 68 rural telephone exchanges in North Dakota from regional provider US West (now CenturyLink). Then, they leveraged federal broadband funds to deploy some of the most extensive fiber networks in the country, turning North Dakota into the rural broadband oasis that it is today.
Download the case study, How Local Providers Built the Nation’s Best Internet Access in Rural North Dakota [pdf].
A Model for Better Rural Connectivity
The case study explores North Dakota's exceptional rural connectivity through several maps and graphs and offers the following takeaways:
Read How Local Providers Built the Nation’s Best Internet Access in Rural North Dakota [pdf].
The fourth edition of our report, Cooperatives Fiberize Rural America: A Trusted Model for the Internet Age, reveals the steady growth of cooperative fiber since we originally released the report in 2017. In the report, we present rural telephone and electric cooperatives as a proven model to connect rural communities across the country with high-quality Internet access. This version updates the maps and analysis in the report with the most recent federal data.
Download the May 2020 update of Cooperatives Fiberize Rural America: A Trusted Model for the Internet Age [pdf].
We first published this report in 2017 and have updated it in the years since. For all versions, including the most current, visit the Reports Archive.
Highlights from the fourth edition of Cooperatives Fiberize Rural America include:
Read the updated version of Cooperatives Fiberize Rural America: A Trusted Model for the Internet Age [pdf].
Earlier this week, Community Broadband Networks Director Christopher Mitchell joined the radio talk show 1A, distributed by NPR, to talk about poor connectivity in rural America and how the Covid-19 pandemic is exacerbating existing digital divides. U.S. Representative Abigail Spanberger from Virginia and ranch owner Tiya Tonn from Kansas also called into the show.
Digging Into the Divide
Christopher and 1A’s other guests explained how rural Americans across the country, from the mountains of Appalachia to the plains of Kansas, struggle with inadequate Internet access. Broadband quality varies greatly, so some households must rely on spotty cell phone hotspots or fast food Wi-Fi networks while neighbors several miles down the road may have access to fiber optic connectivity.

The pandemic is heightening the impacts of the rural digital divide on students and workers who now aren’t able to access their usual connectivity stopgaps, such as public Wi-Fi at libraries and schools. Tiya explained how the shaky broadband connection at her family’s ranch forces her to drive into town for routine activities, and her son spoke to the difficulties he experiences trying to attend online classes now that college campuses are closed.
But poor connectivity isn’t only a rural issue — people who lived near Houston and Columbus, Ohio, called into the show to share how they also can’t access high-speed broadband. Christopher added:
Even just three miles outside Chapel Hill, there are stories in North Carolina about people that are stuck on a technology that hasn’t been upgraded since before the kids that are in high school were born.
How to Expand Access
A recent case study from the Community Broadband Networks initiative at the Institute for Local Self-Reliance (ILSR) finds that rural North Dakotans are more likely to have access to fiber connectivity and gigabit-speed Internet than those living in urban areas. This may surprise many of us city dwellers, who are often stuck with large monopoly providers and their expensive, unreliable Internet access.
The case study, How Local Providers Built the Nation’s Best Internet Access in Rural North Dakota, highlights the efforts of 15 local companies and telephone cooperatives who came together to invest in rural North Dakota and build gigabit fiber networks across the state. Their success is traced back to the companies' acquisition of 68 rural telephone exchanges from monpoloy provider US West (now CenturyLink) in the 1990s. The local providers then leveraged federal funds to connect rural residents and businesses with some of the most extensive and future-proof fiber networks in the country.
Download the case study, How Local Providers Built the Nation’s Best Internet Access in Rural North Dakota [pdf].
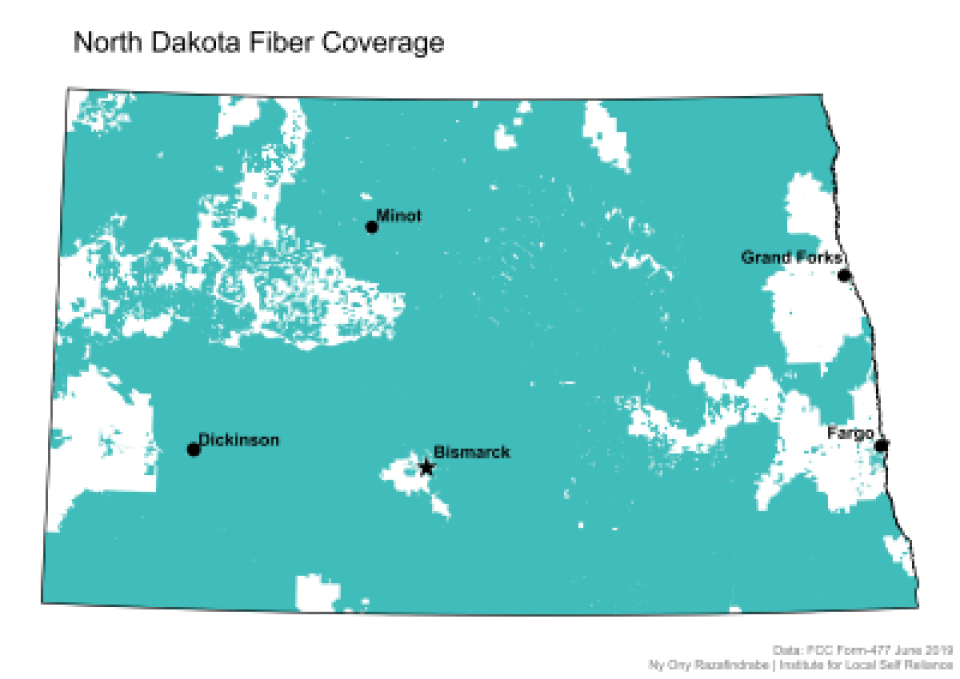
The case study features several maps and graphs that demonstrate North Dakota's widespread, high-quality connectivity, including this map of fiber coverage in the state.
Some key lessons from the case study:
Early last year, Mississippi changed state law to allow electric cooperatives to offer Internet access in addition to electrical service. Since then, several co-ops have announced plans to connect member-owners with fiber optic networks. But despite their new legal authority, some cooperatives are deciding against broadband projects, and their members aren’t happy.
The Daily Journal reported last week on one co-op, Pontotoc Electric Power Association (PEPA), that has chosen not to invest in broadband at this time, citing high costs. PEPA's decision faces strong opposition from some of its members as well as a commissioner from the Mississippi Public Service Commission. Critics claim that cooperative leaders did not fully consider all of the possibilities, and they take issue with the board’s choice to hold the vote during a closed meeting without issuing public notice.
“We’re not adversarial but are advocating for letting the owners get back involved,” Jackie Courson, a PEPA member in favor of broadband, told the Daily Journal.
Critics Question Private Board Vote
The PEPA board decided against moving forward with a broadband network during a private meeting on April 2. Members of the cooperative only found out about the vote four days later, during a public board meeting. In that later meeting, the board limited public discussion on every topic, including the broadband vote, to two people with five minutes each.
As justification for their decision to give the broadband project a pass, PEPA leadership cited the high cost of building fiber infrastructure — estimated at up to $48 million for the northern Mississippi co-op. “One study said it would only be financially feasible after 22 years, and then just marginally. The other two said flat out it was not economically feasible,” PEPA General Manager Chuck Howell explained to the Daily Journal.
Not only has the ongoing Covid-19 pandemic exposed our nation’s dire lack of medical equipment and protective gear, but it has also shone a light on the inadequacy of our rural broadband networks.
A recent CNN article, “Why rural Americans are having a hard time working from home,” by Harmeet Kaur, explores the many struggles that rural households face now that jobs, schools, and everything else has moved online and their outdated broadband connections can’t keep up.
“We Should Be Embarrassed”
CNN reports that while only 1.4 percent of urban Americans don’t have access to broadband speeds of at least 25 Megabits per second (Mbps) download and 3 Mbps upload, more than a quarter of rural households don’t have broadband available to them. And almost three quarters don’t have access to faster upload speeds of 25 Mbps.
These disparate stats are currently on display at parking lots across the country, as families without adequate home connectivity are forced to drive to open Wi-Fi hotspots and sit in their cars while completing assignments for school and work.
The article shared how one teacher in rural Virginia has turned her school’s parking lot into her new office:
Every Sunday since the coronavirus lockdown started, Stephanie Anstey drives 20 minutes from her home in Grottoes, Virginia, to sit in her school's near-empty parking lot and type away on her laptop. Anstey, a middle school history teacher, lives in a valley between two mountains, where the only available home internet option is a satellite connection. Her emails can take 30 seconds to load, only to quit mid-message. She can't even open files on Google Drive, let alone upload lesson modules or get on a Zoom call with colleagues.
“We are the country that created the internet,” Christopher Mitchell, Director of the Community Broadband Networks initiative, said in the article. “We should be embarrassed that millions of people have to drive to a closed library or a fast food restaurant in order to do their jobs or do their homework.”
High Costs, Slow Speeds
The CNN article points to a number of reasons for the dearth of high-quality Internet access throughout rural America.
Last week, Frontier Communications told the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) that there are 17,000 census blocks in which it is now offering 25 Megabits per second (Mbps) download and 3 Mbps upload. This means well over 400,000 Americans now live in areas no longer eligible for the FCC's Rural Digital Opportunity Fund, a $20.4 billion program to expand rural broadband. The first phase will auction off up to $16 billion in subsidies later this year.
In the filing, the company also identified census blocks where it believes other providers will deploy broadband access through state-funded programs, making those locations ineligible for the federal funds as well.
Frontier is Flailing
There’s a belief out there that households don’t really want or need more than a basic broadband connection, much less gigabit connectivity. This mistaken impression especially affects rural areas, where observers point out that a resident may have more fingers on their hand than Megabits per second (Mbps) on their current Internet connection, so surely they’ll be satisfied with a bump up to broadband speeds of 25 or 50 Mbps.
However, in our experience at MuniNetworks.org, demand for high-speed connectivity is actually quite robust in rural areas where the infrastructure exists. We’ve heard from rural cooperatives that many of their fiber network subscribers opt for higher speed tiers and that gigabit take rates near 30 percent in some instances. This suggests rural areas are much more likely than more urban areas to opt for tiers above the lowest cost option.
Even if the majority of rural subscribers don’t need the very highest broadband speeds, it’s important to note that the demand is there and will certainly continue to grow. As federal and state governments invest in rural broadband deployment, they must ensure that the networks they’re subsidizing can meet current and future needs.
Co-ops Feed Need for Speed

Earlier this month, more than 70 electric cooperatives joined consulting firm Conexon in urging the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) to speed up planned rural broadband funds in response to the economic impacts of the Covid-19 pandemic.
In comments filed with the FCC, Conexon called upon the agency to accelerate phase one of the $20.4 billion Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) reverse auction, planned for later this year, in order to connect rural communities and bolster local economies affected by the current crisis. Specifically, Conexon suggested that the FCC expedite RDOF applications and subsidies for providers that plan to build gigabit fiber networks, since under the current auction rules, those bidders are essentially guaranteed funding. The filed comments, available in PDF format below, included an open letter signed by dozens of electric co-op leaders who support the proposal.
While the urgency of rural connectivity has been underlined by the nationwide shutdowns intended to contain the spread of the novel coronavirus, the need for better rural broadband isn’t new. Conexon stated in its comments, “Whether the current health and economic crisis lasts a few months or a year, funding long-term rural fiber networks is necessary and long overdue.”
Proposed RDOF Process
Unlike those who want to postpone RDOF until the Covid-19 crisis passes or the FCC collects more accurate broadband data, Conexon opposes any further delay of the auction. “If anything, in the current economic climate, the RDOF Phase I auction should be accelerated, not delayed,” the company stated.