
Fast, affordable Internet access for all.

Over 140 municipalities in Colorado have opted out of a state law (SB-152) that prevents local governments from investing in broadband infrastructure. With overwhelming support from voters on Election Day last month, Denver, Berthoud, and Englewood became the most recent Colorado communities to bail on SB-152 in the 15 years since Qwest (now CenturyLink) and Comcast successfully lobbied for passage of the anti-local authority bill designed to protect their profits.
While Denver, Berthoud, and Englewood residents ponder next steps, a number of other Colorado communities have already built, or are in the process of building, municipally-owned broadband networks, the most successful example being the NextLight Fiber-To-The-Home (FTTH) network in Longmont.
NextLight, which began building its award-winning FTTH network in 2014, now offers Longmont’s 90,000 residents access to gigabit (1,000 Mbps) service and has surpassed a 50% take rate.
Three other communities in the Front Range region of Colorado are now on the front lines of building municipal broadband networks.
Loveland
Loveland, a city of 76,700 situated in a 25.5 square mile valley at the entrance to Big Thompson Canyon, opted out of SB-152 with 82% voter approval in 2015, a year after Longmont began building its fiber network 17 miles south of the “gateway to the Rockies.”
Over the past five years, the Loveland Water and Power Department has been planning, and now building, its own Pulse fiber network.
To finance the project, city officials opted to issue $95.5 million in bonds. The bonds are backed by Loveland’s electric utility, which serves 37,500 residential and commercial accounts.

It’s been 15 years since Colorado passed SB 152, the state law intended to restrict communities from building and managing their own broadband networks. A great deal has happened since: more than 140 communities have voted to opt out of the law, and networks like Longmont’s NextLight have been success stories in municipal Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH).
In this episode Christopher talks to Ken Fellman and Geoff Wilson. Ken and Geoff were at the heart of the story back in 2005. They describe how Qwest (now CenturyLink) along with Comcast used legislative allies to introduce the anti-local authority bill aimed at protecting their profits. They share how the monopoly Internet Service Provider’s (ISP) lobbyists helped push two false narratives that we’ve seen many times before: that the bill sought to “level the playing field” so that private companies could compete with municipally run networks, and that SB152 “protected” Coloradoans from irresponsible local governments.
Christopher, Ken, and Geoff unpack the nuance of such arguments, which monopoly ISPs have used time and time again around the country, that place prohibitive burdens on local actors. They also cover developments over the last decade and a half, and talk about how while SB 152 had a negative impact on the development of municipal networks and broadband infrastructure in the short-term, we might consider how the long-term has shown how so many Colorado communities were compelled to action.
We’ve covered Colorado’s SB 152 a number of times in the past. Recently, the first phase of middle-mile network Project Thor turned on, introducing redundancy and bringing cost savings with it. Glenwood Springs, the first community to opt out, is in the process of extended its own FTTH network citywide.
This show is 60 minutes long and can be played on this page or via Apple Podcasts or the tool of your choice using this feed.
Transcript below.
We want your feedback and suggestions for the show-please e-mail us or leave a comment below.
Listen to other episodes here or view all episodes in our index. See other podcasts from the Institute for Local Self-Reliance here.
Thanks to Arne Huseby for the music. The song is Warm Duck Shuffle and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (3.0) license.
Lighting up the first phase of middle-mile network Project THOR isn’t the only good news coming out of northwest Colorado recently. Glenwood Springs, a city of 10,000 forty-five minutes north of Aspen, is once again looking to secure the future of its information infrastructure.
In a recent 6-1 decision, the city council voted to replace and expand the reach of its existing fiber system, which currently serves businesses and a select number of residents. The resulting network of 150 miles is projected to cost around $9 million and take two years to complete. Once done, current users will be switched over with no disruption. The new network will be citywide and have the capacity to handle Glenwood Springs’ 4,800 residences and commercial premises. Hopes are, many will sign up.
Building up a Fiber Legacy
This isn’t the first time Glenwood Springs has taken such initiative. Almost twenty years ago the city had access to speeds below one megabit per second (Mbps) and — after being told by Qwest (now CenturyLink) there were no plans for investment or upgrades — it built its own fiber backbone to community anchor institutions with a wireless overlay to provide service to residential customers. The city later expanded the fiber network to connect businesses and some households and opened up the network for participation by private Internet service providers (ISPs).

After a bitter battle with Comcast and a successful referendum to reclaim local authority back in 2017, Fort Collins, Colorado, is moving forward with its municipal fiber network, Connexion. The city is starting to connect residents to the network, so we wanted to check back in with local activists and Connexion staff to find out how it's going. In this episode, Christopher interviews community advocates Glen Akins and Colin Garfield as well as Colman Keane, Connexion executive director, and Erin Shanley, Connexion marketing manager.
Glen and Colin discuss their grassroots organizing efforts from the 2017 referendum, and they share what it's like to finally watch the network being built. Colin, who has Internet access from Connexion now, describes the installation process for his new fiber service. The pair also tell Christopher how incumbent providers are reacting to the municipal network.
Speaking from the city's point of view, Colman and Erin explain how Connexion differs from other municipal networks, including that it faces competition from other broadband providers in Fort Collins. Christopher praises the city's decision many years ago to underground all utilities, and Colman tells Christopher how that has introduced challenges to the network fiber build. Erin shares how the Connexion is marketing services and engaging with the community, while keeping information away from competitors and staying mindful that the network isn't yet available citywide.
For more on Fort Collins and Connexion, listen to Community Broadband Bits Episode 211: Fort Collins Mayor on Fort Collins Fiber Future and Episode 282: Organizing for a Community Network, Against Big Cable
This show is 46 minutes long and can be played on this page or via Apple Podcasts or the tool of your choice using this feed.
Transcript below.
We want your feedback and suggestions for the show-please e-mail us or leave a comment below.
Listen to other episodes here or view all episodes in our index. See other podcasts from the Institute for Local Self-Reliance here.
Thanks to Arne Huseby for the music. The song is Warm Duck Shuffle and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (3.0) license.
Even though there are more than 140 municipalities and counties that have voted to reclaim local telecommunications authority from the state, the City and County of Denver, Colorado, has put off such a referendum. 2020, however, may be the year that the metropolitan region votes to shed themselves of the harmful restrictions of SB 152.
Councilman Paul Kashmann announced earlier this month that he supports the city taking the question to the voters, like so many other local leaders have already done in Colorado. He suggests putting it on the 2020 ballot. At a policy committee on October 9th, Kashmann told his colleagues:
“Make no mistake that the Internet is much more than Netflix and Facebook and Twitter and Minecraft and the like,” Kashmann said. “The Internet is truly … the library of the 21st century. It’s the entry point into the world of information in the same way as our traditional brick-and-mortar libraries have been for centuries.”
 Comcast and Centurylink provide Internet access to the community of around 620,000 people. Even though the large corporate providers tend to concentrate their investments in urban areas like Denver, the issue of affordability still keeps many urban dwellers on the wrong side of the digital divide.
Comcast and Centurylink provide Internet access to the community of around 620,000 people. Even though the large corporate providers tend to concentrate their investments in urban areas like Denver, the issue of affordability still keeps many urban dwellers on the wrong side of the digital divide.
The Denver Public Library lends out between 115 - 120 mobile hotspots and the wait list can extend as long as 200 names at a time. Libraries from which the hotspots are most often borrowed tend to be in areas where fewer people have home Internet access. The library estimates that approximately 20 percent of the city’s residents aren’t connecting at home.
Kashmann stated that he’s anticipating pushback from incumbent Internet access providers. He looks on the measure as in the same light as any other necessary utility:
Last week, Trustees in Estes Park, Colorado, unanimously voted to change the community’s municipal code in order to bring constituents what they want — a publicly owned broadband network.
Strong Support
It’s been four years since 92 percent of voters in Estes Park chose to opt out of the state’s restrictive SB 152. By reclaiming local telecommunications authority through the opt out referendum in 2015, the mountain town of approximately 6,300 residents was able to explore possibilities for better connectivity.
After several days-long outages caused by lack of redundant infrastructure in the area, local business leaders and town officials knew it was time to take control of the situation. Surveys in the community revealed that approximately two-thirds of respondents want better connectivity in the community and of those respondents, 40 percent consider it the most important service the town can offer.
Recently, local editors from the Trail Gazette echoed the sentiments of the community and urged community leaders to end discussion and take action:
…Estes Park needs more action and less discussion for greater access to information and global connectivity. No longer is accessible, fast and reliable broadband Internet a luxury; it is a necessity in our digital world.
Prior to the March 12th vote, the Broad of Trustees opened up the meeting to allow comments from the public. In addition to Trustees’ questions about economic development, reliability, and potential capacity of the proposed infrastructure, residents stepped forward to voice their opinions.
Not one citizen spoke out against the project.
Town resident Michael Bertrand, who works as an asset manager for a real estate investment firm and works remotely, opened up public comment with a statement in favor of the project. "I need reliable internet," Bertrand said. "I've had fiber in other locations in the past and it's incredible. The speeds you get are just fantastic."
A total of 40 counties and 102 municipalities have now chosen local telecommunications authority by passing ballot measures to opt out of restrictive state law. Last November, 18 counties, cities, and towns voted to join the expanding list of communities opting out of SB 152, which revoked local telecommunications authority in 2005. We decided to update our map to get a new visualization of what the situation now looks like in Colorado.
Take a gander:
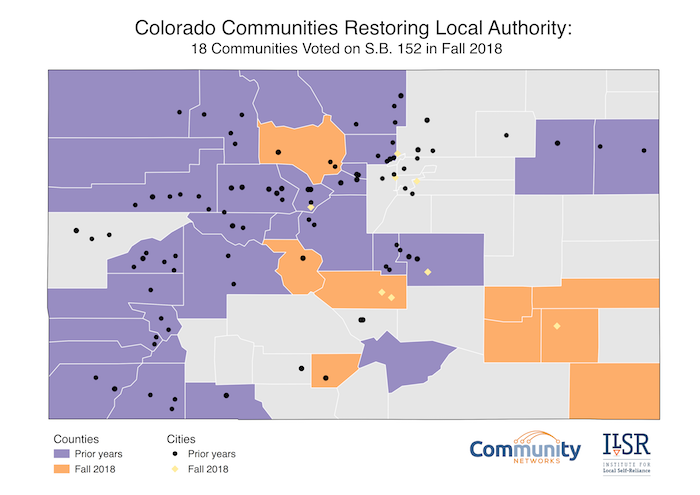
Moving Across the State
The map, updated by Intern and Mapping Maven Hannah Bonestroo from an earlier version created by former Research Associate and Visualization Virtuoso Hannah Trostle, shows how the decision to opt out is sweeping from region to region. Earlier referendums centered in the Mountain and into the Western Slope and San Luis Valley communities. During this past election cycle, most of the counties bringing the issue before voters were in the Plains region.
In past years, mountain towns, often resort communities, were looking for better connectivity when big ISPs considered deployment too challenging and expensive in their geographies. Now, it appears that the rural and less populated Plains communities are seeing value in reclaiming local authority.
With fewer population centers in the Plains region, farms and ranges fill much of this section of the state. Large, corporate ISPs don’t consider this type of landscape profitable due to the lack of population density, however, farmers and rangers require high-speed Internet access for various reasons. Crop and livestock monitoring and realtime reporting are only a few of the ways 21st century agricultural professionals use broadband.
Colorado’s Free Communities
In Colorado, there are 271 active incorporated municipalities, 187 unincorporated Census Designated Places (CDPs) and other small population centers that are outside of CDPs or municipalities. To date, the 102 municipalities that have elected to opt out of SB 152 have all been incorporated municipalities, or approximately 38 percent.
The march toward reclaiming local telecommunications authority throughout Colorado continued yesterday as eighteen more communities opted out of restrictive SB 152. As in prior years, voters passed referendums with high majorities in every contest.
It’s a Sweep
Once again, local voters emphatically expressed support to step out of the weight of SB 152 and put decision making for local connectivity in their own hands. The lowest passage for this cycle was 62 percent of the vote in Crowley County; the highest occurred in the town of Blue River where 90 percent of voters chose to opt out. Average passage for all 18 referendums came to just under 76 percent of the vote.
We’ve already reported on ballot measures in the municipalities of Aurora, Cañon City, Florence, Fountain, and Erie. Here’s how the “yes” votes shook out in those communities (please note that these numbers are considered “unofficial” and we round up to whole percentages):
Other cities and towns which we recently learned were taking up the issue also passed the opt out issue by wide margins:
Counties that we’ve been watching also came out positive. Thanks to Virgil Turner, who is the Director of Innovation and Citizen Engagement for the City of Montrose, Colorado, (and our eyes in the state) we found out that this was a year when the majority of referendums happened at the county level.
Within Colorado’s 64 counties, a total of 40 have brought the opt out question to their voters; all referendums passed. Now, 62.5 percent of counties in the state are free of SB 152, leaving only 37.5 percent or 24 counties subject to the harmful law.
Fixing Past Mistakes For Different Futures
Breckenridge was among the list of Colorado communities that voted to opt out of the state’s restrictive SB 152 back in 2016. Now, they’re ready to move forward with design and construction of an open access network. As the resort town prepares to begin work on their fiber infrastructure, several other communities will ask voters to opt out of SB 152 on November 6th.
To the Voters
As we reported in August, Aurora, Cañon City, the town of Florence, and Fremont County had already made plans to put the opt out question on their local ballots. Since then, we’ve discovered that that at least six other local governments want voters to address SB 152.
In Salida, where the town needed to fill a vacated office without delay, community leaders chose to hold their election in September and put the issue on the ballot. The measure to opt out passed with 85 percent of the vote.
Voters will also decide of their towns or counties should reclaim local telecommunications authority in the towns of Fountain and Erie along with Chaffee County and Kiowa County. Over the past several years, more than 120 local communities have asked voters to opt out of SB 152 and local referendums overwhelmingly passed. Many local communities have presented the issue to voters with no specific plans in mind, but do so in order to keep their options open and because they feel that Denver is less qualified than they are in making decisions related to local connectivity.
The Fremont Economic Development Corporation (FEDC) has reached out to voters, urging them to approve the measure with a "yes" vote. The fact that SB 152 still hangs like cloud over the region prevents them from obtaining grant funding to boost economic development.
Local fall referendums are still a few months away, but at least four additional Colorado communities have decided to put local broadband authority on the ballot. In addition to Aurora, Cañon City, and Florence, Fremont County will ask voters to opt out of SB 152.
In 2005, Colorado's state legislature passed the bill, removing local communities' authority to take steps to use publicly owned infrastructure to offer telecommunications services either directly or with a private sector partner. The law, however, allows communities to hold a referendum so voters can choose to "opt out" as a way to reclaim that authority. Over the past several years, cities, towns, and counties by the dozen have overwhelmingly passed measures to opt out. Some have a specific plan in place to develop networks, while others want to preserve the option. Each fall and spring, more communities put the issue on the ballot.
Florence
We spoke with City Clerk Dena Lozano in the small town of Florence who confirmed that voters there will be deciding the issue in November. With less than 3,900 people in Florence, almost 40 percent of residents work in either education or public administration. The town began as a transportation center at the base of the Rocky Mountains; three railroads that transported coal converged there. Later, the town became known as the first oil center west of the Mississippi.
Today, the town has a downtown antique market and has worked on nurturing its culinary dictrict. They've also established an Urban Renewal Authority to help keep their town center on a positive track. Within their 2017 Master Plan, Florence leaders tackle their wish to allow the art and business communities to grow while still maintaining the small town charm that keeps many residents in Florence.
Cañon City