
Fast, affordable Internet access for all.


In this podcast episode, Christopher engages in a conversation with Philip Neufeld, the Executive Officer for Information Technology at the Fresno Unified School District. They delve into the crucial role of data in addressing broadband connectivity challenges in low-income neighborhoods, stressing the need for accurate and comprehensive data to guide policy decisions and investment strategies.
Philip's proactive data collection efforts in Fresno, particularly through speed tests on school devices, offer valuable insights into connectivity issues. He emphasizes the importance of using this data to advocate for solutions that bridge the digital divide.
The episode concludes by exploring the limitations of current mapping methods and the urgent need for more accurate data to drive effective and targeted solutions. Highlighting a collaborative approach, they underscore the significance of public-private partnerships and community coalitions in advocating for equitable broadband access in low-income neighborhoods.
This show is 44 minutes long and can be played on this page or using the podcast app of your choice with this feed.
Transcript below.
We want your feedback and suggestions for the show: please e-mail us or leave a comment below.
Listen to other episodes here or see other podcasts from the Institute for Local Self-Reliance here.
Thanks to Arne Huseby for the music. The song is Warm Duck Shuffle and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (3.0) license.
*In partnership with Broadband Breakfast, we occasionally republish each other's content. The following story by Broadband Breakfast Reporter Teralyn Whipple was originally published here.
South Carolina’s innovative state broadband map can accurately identify areas of over-reporting by Internet service providers (ISPs), the director of the state’s broadband office said in a recent Ask Me Anything! session in the broadband community.
South Carolina processes the same data as does the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) as it creates its broadband map.
However, it also performs audits on the ISPs to ensure they are submitting accurate data. Hence, the state can determine errors in reporting data based on where the ISP’s networks had been deployed previously and where state investments have gone, said Jim Stritzinger, director of the state’s broadband office.
Providers are required to file amended returns with the FCC in the event that South Carolina’s state broadband office flags errors in their reporting information. Errors include misreporting of technology types.
If the reporting errors are not corrected, the state will report the defaulting ISP to the FCC, said Stritzinger, a software engineer with a passion for mapping broadband in the Palmetto state.
A big flaw of the FCC’s maps is that ISPs were able to report advertised speeds, which Stritzinger said were useless.
Written by Christine Parker and Ry Marcattilo-McCracken
A recent report by BroadbandNow made the rounds in February, with the authors concluding that the average price for broadband access across all major speed tiers for Americans has fallen, by an average of 31 percent or nearly $34/month, since 2016. At a glance, this is great news – perhaps affordable Internet access for all is within reach?
Readers following up to check out the report itself would be well justified in coming to the same conclusion, with BroadbandNow writing in the first paragraph that “we’ve found that prices have decreased across all major download speeds (25Mbps up to 1Gbps+) and technologies (cable, fiber, DSL and fixed wireless).” Immediate news coverage reinforced the report’s points.
But you don’t have to follow broadband policy closely to get the sense that something a little off is going on here. It feels like every day there’s a story like this one about Cable One, with a provider increasing speeds as it improves its network infrastructure and then raising rates while removing the slowest tier options. Charter and Comcast, for their part, do this nearly every year whether pairing it with speed increases or not. Is broadband access getting cheaper, or more expensive? What’s going on here?
The reality is that this report from BroadbandNow, unfortunately, poorly frames the national broadband marketplace. At best, it muddies the waters with a lack of clarity about the relationship between broadband access speed tiers and relative pricing. At worst, it leaves the average reader with the incorrect assumption that broadband prices must be falling, and gives the monopoly cable and telephone companies ammunition to push for millions more in taxpayer dollars while building as little new infrastructure as possible.
After three years in a row with similar results, PCMag’s “Fastest ISPs in America” for 2021 analysis shows a clear trend: community owned and/or operated broadband infrastructure supports networks which, today, handily beat the huge monopoly Internet Service Providers (ISPs) - cable and telephone alike – for sheer speed.
The latest list proves it. Of the ten-fastest ISPs in the country, all of them feature operators that either are cities themselves or use city-owned fiber or conduit to deliver service across whole or parts of their footprint.
City-run networks making the list again this year include Longmont, Colorado (third); Chattanooga, Tennessee (sixth); and Cedar Falls, Iowa (seventh). Cedar Falls topped the list last year, but all three networks are regulars over the last three analyses done by the outlet. Broken down regionally, they are also joined by other municipal networks around the country, including FairlawnGig in Ohio and LUS Fiber in Louisiana.
Tired of waiting for connectivity solutions to come to town, one Minnesota community has instead partnered with a local telephone cooperative to build a fiber network reaching every home and business in the city.
In embarking on its journey to improve local Internet access six years ago, Long Prairie (pop. 3,300) ended up partnering with one of the most aggressive fiber network builders in the state - Consolidated Telephone Company (CTC) - on a solution that meets local needs. The two finished a ubiquitous Fiber-to-the-Home build in 2018, with CTC now owning and operating the network.
Looking for Solutions
The City of Long Prairie (pop. 3,300), the county seat in Todd County, Minnesota, has long struggled with connectivity. It has manifested in issues with connecting students from their homes, with losing parts of the local workforce, and in a lack of access to support larger healthcare institutions for their aging population.
In 2014, the city met with state officials as well as broadband providers to discuss the results of a feasibility study that was done back in 2011. Todd County stressed that this was a pressing issue that couldn’t wait anymore - they needed state support with funding and potentially help setting up a partnership with a local co-op. But this kind of partnership couldn’t just be with any co-op, it had to be a mutually beneficial partnership that could connect all of Long Prairie’s businesses and residents. It would take 2 more years before the community entered into an agreement with the right one.
CTC started in the 1950s as a telephone cooperative, and began offering Internet access via DSL service in the late 1990s and early 2000s. Around 2008, CTC’s Board of Directors decided that the best long-term strategy for providing strong, reliable connectivity would be to build out Fiber-to-the-Premise (FTTP) for all of its members.
Building on that initial network, the main vision and mission driving the co-op over the last 10 years has been getting as many people in the area fast and reliable connectivity as possible. But because CTC is just one firm, that has meant developing relationships with other towns, cities, and counties that bloom into successful partnerships.
Snapshot
Colorado House passes bill that reduces broadband board membership and conceals mapping data
Michigan legislature approves bill granting ISPs property tax exemptions
New Mexico and Virginia bills await governors’ action
The State Scene
Tennessee
Tennessee is home to some of the most creative local solutions to bridging the digital divide. Municipal fiber networks across the state, including Chattanooga’s EPB Fiber network, Morristown’s FiberNet, and Bristol’s network, have been a boon to economic development, job creation, educational initiatives, and overall quality of life in the past decade.
The next city to potentially join the ranks of providing municipal broadband in Tennessee is Knoxville. On March 11, the Knoxville Utility Board approved a business plan to provide Internet services across its service area.
Despite the widespread success of municipal networks across Tennessee, the state restricts what populations they can serve. Although Tennessee law allows cities and towns to offer advanced telecommunications services if they have a municipal electric utility, the networks are not permitted to offer those services to residents who live outside of the utility’s service area. Removing these restrictions would permit substantial fiber expansion to connect more residents at no cost to the state or taxpayers.
Fed up with poor speeds and no service, a handful of residents in Washington County, Ohio have teamed up to form a broadband cooperative to pursue better connectivity for themselves and their neighbors.
The Southeast Ohio Broadband Cooperative (SEOBC), created last May, is the result of work led by David Brown. “Electric cooperatives worked,” he said of the founding impulse. “Why can’t we do the same thing for broadband?”
After organizing, the first step the group took was to set up a speed test and map to both show how poorly connected many residents of Washington County are, and to plan for the future. That test is still ongoing, and the results are not terribly encouraging so far. Out of 4,662 run, almost 800 premises have no service (17%). Suddenlink and Charter are the only providers returning averages above the FCC’s threshold for basic broadband (25/3 Mbps (Megabits per second)), but together they represent just over 10% of those taking tests — though admittedly this is the result of sample bias, the map shows that outside of Marietta, Lovell, Beverly, Vincent, and the few other concentrated areas there are few providers returning adequate speeds. Subscribers to Frontier, Windstream, and ViaSat across the county see average connections of around 8/2 Mbps (Megabits per second). Those on HughesNet even worse off, at 3/2.5 Mbps.
Asa Boring, a Belpre Township trustee, told the Marietta Times:
We have people in our area who have sort of Internet, but it’s kind of a hit and miss thing. But when you get a mile out of Little Hocking it’s over with, you just don’t get it . . . unless you sign up with Windstream and sometimes it works and sometimes it doesn’t.
Targeted Solutions
If you live in the land of ten thousand lakes, your help is needed. The Minnesota Rural Broadband Coalition has launched a speed test initiative to collect much-needed data from everyone in the state so that lawmakers and stakeholders can better direct broadband expansion efforts now and in the future. Hop over to the speed test page and give them a hand.
Data, Data, Data
The Minnesota Rural Broadband Coalition (MRBC) — which is made up of over a hundred utilities, cooperatives, regional development commissions, nonprofits, private companies, and rural and urban interest groups — has worked for years with local communities and in the state capitol to advocate for more funds and help local communities address Internet access imbalances across the state. The initiative is the latest mark of their efforts, asking Internet users to input their addresses and how much they pay their Internet Service Provider (ISP) to get a better sense of speeds, availability, and prices.
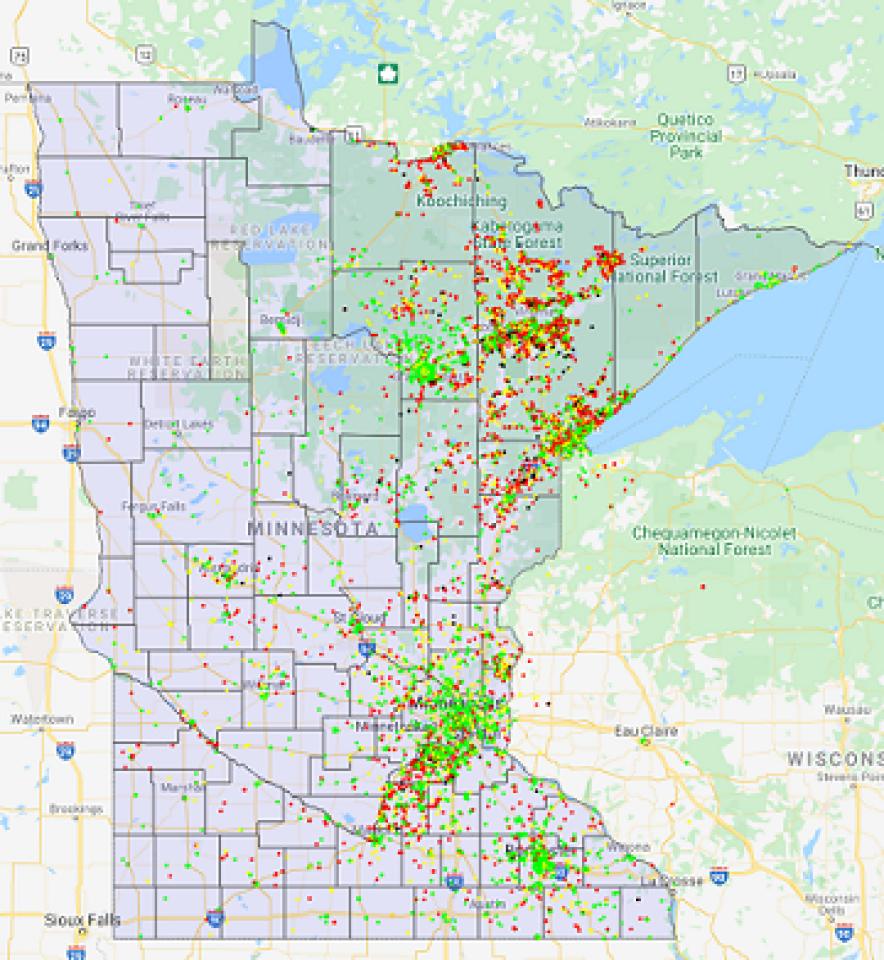
To date, they’ve gotten results from a little over 15,000 tests in 11,000 locations. There are predictable problem areas in the northeast part of the state, and according to the map just under 7% of locations are unserved so far. Saint Louis, Itasca, and Carlton Counties account for the bulk of the tests outside of the metro area, though Minnesotans in Scott and Le Sueur Counties south of the 169 corridor are also putting up a strong showing.
This is the tenth year that PCMag has conducted its Fastest Internet Service Providers (ISPs) test, and it comes at a time when tens of millions more Americans across the country are working from home. This time, the results show two significant categories of winners — municipal networks and private-sector ISPs using publicly owned fiber or conduit — which says a lot about the state of high-speed Internet. Like last year, municipal networks and their private-sector partners, along with locally-owned providers, dominated the rankings.
PCMag’s methodology doesn’t seem to have changed much in 2020. Using a customized tool, the outlet tests ping, jitter, and per-second data throughput on the download and upload side of things. The results are weighted 80% towards download and 20% towards upload. From June 1st to June 2nd, 443,940 tests were completed, with the magazine ruling out non-U.S. benchmarks for a final aggregation of 358,358 tests. The minimum threshold to earn a place on the list is 100 tests, and PCMag breaks down the results in two major categories: Fastest Major ISP (those with at least a million subscribers) and Fastest Overall ISP. Read the full report here.

Cedar Falls Utilities Dominates
Since 2011, PCMag has collected speed data and written about the country’s Fastest ISPs based on download and upload results. This year’s results reflect, once again, that locations with publicly owned broadband infrastructure contribute to communities’ ability to offer faster connectivity.
How They Did It
PCMag asked readers to use a special speed test developed specifically for this reporting that measured download and upload speeds. PCMag's Speed Index assigned to each ISP represented 80 percent download speed and 20 percent upload speed. Filtering out non-U.S. tests, they ended up with 256,016 tests that applied to the comparisons. If, however, a location (for state and regional comparisons) or ISP had fewer than 100 tests, the folks at PCMag did not consider it a contender.
While editors further broke down results so as to stack major ISPs against each other in a head-to-head comparison, they also looked at all the results in a general comparison. PCMag broke down the results further by region and city. For more details on the results, check out the full article.
Munis New and Not-So-New
FairlawnGig in Ohio made the list this year, adding a third municipal Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) network to the list. The city’s retail service began serving residents with gigabit connectivity back in 2017, after firmly establishing their fiber services for local businesses.
When contemplating the investment, city leaders adopted the approach that their fiber optic network would be an essential piece of infrastructure on par with sewers or roads. Fairlawn used municipal bonds with no intention of turning a profit; they considered the network an investment that would keep the Akron suburb competitive. Residents, businesses, and institutions in Fairlawn, however, have enthusastically signed up for fast, reliable, connectivity where residents can get gigabit Internet access for $75 per month.