
Fast, affordable Internet access for all.

On January 18th, the FCC ended months of speculation and released a fact sheet that included several key conclusions to be included in the 2018 Broadband Deployment Report. The most important is that the FCC continues to recognize that mobile Internet access is not a substitute for fixed access. The Commission has also decided to leave the definition of broadband at 25/3 Mbps (down/up).
“Broadband” Will Not Slow Down
The Commission had proposed reverting to a slower definition of broadband from the current standard of 25 Megabits per second (Mbps) download and 3 Mbps upload. Under Tom Wheeler’s leadership, the FCC decided to update the standard to its current definition in January 2015, but current Chairman Ajit Pai and other Republican Commissioners suggested in last year’s Notice of Inquiry (NOI) that the FCC might effectively take us backward to a 10 Mbps/1 Mbps standard.
The suggestion rankled better connectivity advocates and Internet users. Many recognized that lowering the standards would make it easier for the FCC to proclaim that the U.S. was making strong progress toward universal household deployment. The Commission would have been justified making such a conclusion under the standard because large sections of rural American receive DSL, fixed wireless, satellite, or mobile Internet access that would meet a lowered 10/1 standard.
Hundreds of thousands of people, organizations, and businesses filed comments opposing a slower standard. Many of them live in areas where 10/1 speeds are already available but who have been waiting for better options. Commissioners Rosenworcel and Clyburn also spoke out against the lowering broadband speeds.
Commissioner Rosenworcel tweeted:
Ever since the FCC reversed network neutrality protections, an increasing number of local communities have started to wonder about the advantages of publicly owned Internet infrastructure, including conduit. At the Institute for Local Self-Reliance, we’ve received an uptick in requests for information from elected officials, community business leaders, and local citizens.
When folks are similarly curious about public-private partnerships, they wonder about whether or not a municipality or other form of local government can require a private sector partner ISP to adhere by the tenets of network neutrality. An agreement between public and private sector partners to bring better connectivity to a city or region is a contract between the involved parties; the FCC’s decision won't interfere.
Looking At Lincoln
Lincoln, Nebraska, has fine-tuned the art of working with private sector partners interested in using their publicly owned conduit for privately owned fiber. The city invested in an extensive conduit system back in 2012 to create an environment that would welcome private sector providers. Nelnet’s ALLO Communications uses the conduit to offer Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) in Lincoln.
The city uses a Broadband Franchise agreement to allow ISPs non-exclusive use of their publicly owned conduit. In Section 4: Service Characteristics, Lincoln requires any private sector ISP that wishes to use their conduit to adhere by network neutrality rules, which they clearly spell out. You’ll notice that the city also imposes a “no data caps” rule:
Section 4: Service Characteristics.
A. The System shall, at a minimum, provide the following capabilities and characteristics:
1.Net Neutrality: In the provision of Broadband Service, Franchisee shall comply with the Open Internet regulations.
2.No Blocking: Franchisee shall not block lawful content, applications, services, or non-harmful devices; and
3.No Throttling: Franchisee shall not impair or degrade lawful Internet traffic on the basis of Internet content, application, or service, or the use of non-harmful devices; and

The FCC collects data from Internet Service Providers that reflects census blocks where they offer service to at least one premise. Currently, the Commission does not collect information about rates subscribers pay. A new report from the Berkman Klein Center dives into prices subscribers pay and also looks at trends from national companies as well as local publicly owned networks. The report, Community-Owned Fiber Networks: Value Leaders in America, supports what we’ve always found — that publicly owned networks offer the best all around value for the communities that make the investment. Download the report.
In the Abstract, authors David Talbot, Kira Hessekiel, and Danielle Kehl describe their approach:
We collected advertised prices for residential data plans offered by 40 community-owned (typically municipally owned) Internet service providers (ISPs) that offer fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) service. We then identified the least-expensive service that meets the federal definition of broadband—at least 25 Mbps download and 3 Mbps upload—and compared advertised prices to those of private competitors in the same markets. We found that most community-owned FTTH networks charged less and offered prices that were clear and unchanging, whereas private ISPs typically charged initial low promotional or “teaser” rates that later sharply rose, usually after 12 months. We were able to make comparisons in 27 communities. We found that in 23 cases, the community-owned FTTH providers’ pricing was lower when averaged over four years. (Using a three year-average changed this fraction to 22 out of 27.) In the other 13 communities, comparisons were not possible, either because the private providers’ website terms of service deterred or prohibited data collection or because no competitor offered service that qualified as broadband. We also made the incidental finding that Comcast offered different prices and terms for the same service in different regions.
The FCC collects data from Internet Service Providers that reflects census blocks where they offer service to at least one premise. Currently, the Commission does not collect information about rates subscribers pay. A new report from the Berkman Klein Center dives into prices subscribers pay and also looks at trends from national companies as well as local publicly owned networks. The report, Community-Owned Fiber Networks: Value Leaders in America, supports what we’ve always found — that publicly owned networks offer the best all around value for the communities that make the investment.
Download and read the full report here.
In the Abstract, authors David Talbot, Kira Hessekiel, and Danielle Kehl describe their approach:
We collected advertised prices for residential data plans offered by 40 community-owned (typically municipally owned) Internet service providers (ISPs) that offer fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) service. We then identified the least-expensive service that meets the federal definition of broadband—at least 25 Mbps download and 3 Mbps upload—and compared advertised prices to those of private competitors in the same markets. We found that most community-owned FTTH networks charged less and offered prices that were clear and unchanging, whereas private ISPs typically charged initial low promotional or “teaser” rates that later sharply rose, usually after 12 months. We were able to make comparisons in 27 communities. We found that in 23 cases, the community-owned FTTH providers’ pricing was lower when averaged over four years. (Using a three year-average changed this fraction to 22 out of 27.) In the other 13 communities, comparisons were not possible, either because the private providers’ website terms of service deterred or prohibited data collection or because no competitor offered service that qualified as broadband. We also made the incidental finding that Comcast offered different prices and terms for the same service in different regions.

With the Federal Communications Commission Republicans poised to redefine broadband to include slow, unreliable, and often bandwidth-capped mobile service, we talk with two high school students from southeast Ohio, Herron Linscott and Lilah Gagne, that have succeeded despite the lack of fixed broadband access in their homes. Soon the FCC may include those homes as having broadband though they clearly don't fit the description of what any sane person would call advanced telecommunications.
We start off episode 287 of the Community Broadband Bits podcast with Next Century Cities Executive Director Deb Socia, who reminds us why mobile Internet access is not an adequate subsitute for fixed access. Next Century Cities has launched the Mobile Only Challenge - share MobileOnlyChallenge.com around - to highlight the challenges of relying solely on mobile Internet access.
We then talk to Herron Linscott and Lilah Gagne about their experiences in southeast Ohio as high school students without home fixed Internet access. Both have had to schedule lots of time away from home in order to complete assignments and partake in extra-curricular activities and both offer a window into the importance of connectivity for the next generation.
This show is 25 minutes long and can be played on this page or via Apple Podcasts or the tool of your choice using this feed.
Transcript below.
We want your feedback and suggestions for the show-please e-mail us or leave a comment below.
Listen to other episodes here or view all episodes in our index. See other podcasts from the Institute for Local Self-Reliance here.
Thanks to Arne Huseby for the music. The song is Warm Duck Shuffle and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (3.0) license.
A holiday poem in the style of "How The Grinch Stole Christmas" by Dr. Seuss.
Every American on the Internet liked network neutrality a lot
But the FCC’s Grinchy Pai, former lawyer for Verizon, did not!
Pai hated net neutrality! He despised it, he dreaded it!
And on December 14th, he and his cronies, they shredded it.
It could be, perhaps, that he wanted more dough.
ISPs could make more with lanes fast and lanes slow.
But whatever the reason, cash or prestige,
His choice pissed off subscribers by many degrees.
Americans cried out in anger and dismay!
“We like net neutrality! Don’t take it away!”
“It’s good for free speech and new businesses too! Selling, reporting, and artistic debut!
We need it for school kids who have tests to take.
We need it for far away doctors with prognoses to make.
We need it so businesses can hit the ground running.
We need it for working from home, for homework, for funning.
We need it to save money. To get good Internet service.
We don’t want ISPs to decide what to serve us.”

“You have market protection,” he said with a snort.
But ILSR elves proved there was nothing of the sort.
The elves showed very little, almost no competition.
But Grinchy Pai didn’t care for the net neutrality tradition.
He wouldn’t listen to pleas to stop and investigate.
Even millions of fake comments didn't make him hesitate.
His planned to kill net neutrality completely.
His overlord ISPs would reward him so sweetly.
“Pooh-pooh to subscribers!” he was grinchily singing
It wasn’t long after FCC Chairman Ajit Pai and the other Republicans on the Commission rescinded network neutrality protections that murmurs began to rise about the future role of municipal networks. Soon, journalists reporting on tech issues began contacting us for comment about the intersection between network neutrality and publicly owned Internet network infrastructure.
The day after the FCC decision, Christopher appeared on This Week in Enterprise Tech (TWiET) with Fr. Robert Ballecer for episode 269, “After Net Neutrality.” Christopher’s segment of the show starts at around 14:16 and finishes around 44:22. Fr. Ballecer comments that, while municipal networks were of interest in the past, now that network neutrality protections have been revoked, they are a more urgent possibility.
Christopher shared some of the data we’ve discovered that reveals how very little competition actually exists, even though the FCC uses market protection as a crutch for dismantling network neutrality. The guys also discuss local franchises and how they helped to encourage deployment, limits to local franchises that exist in certain states, and existing telecommunications monopolies.
Even though municipal networks typically adopt policies that adhere to network neutrality standards, there remains a question of what will happen when those network connect to the middle mile, often controlled by companies known to by network neutrality violators. The hosts and Christopher speculate on whether or not publicly owned networks can create the competition needed to put the big companies on their best behavior. They also get into wireless vs. mobile vs. fiber and the struggle to accept the need for complements. Christopher offered some tips on ways to initiate a grassroots movement for a muni network initiative and creative early steps to situate a community favorably for a future network.
Check out the conversation:
In addition to shredding network neutrality, the FCC is making it more difficult for us to obtain high-quality Internet access. Under the Obama administration, the FCC raised standards for broadband, but the new administration is set on driving us backward. Chairman Ajit Pai and the other Republicans in the FCC want to equate mobile Internet service with home connections. They also want to revert to a slower definition of broadband. We have to show them that their plan is ludicrous and shortsighted; the #MobileOnly Challenge is a start.
What Is The #MobileOnly Challenge?
It seems as if Pai and his chums aren’t aware of what it’s like to depend solely on a mobile connection, especially for people in places where mobile service is spotty or slow. In order to share the experience, the Institute for Local Self-Reliance, along with nine other organizations and FCC Commissioners Clyburn and Rosenworcel, are supporting the #MobileOnly Challenge.
For one day in January, participants will put away their laptops and use only their smartphones to access the Internet. During the day, they will report on their experience via social media with #MobileOnly in the tweet, FB post, Instagram post, or other notification about the experience.
The FCC expects to vote on the mobile Internet access and broadband definition question by February 2, 2018. Right now, the Commission defines broadband as 25 Mbps download and 3 Mbps upload; they want to redefine that speed to 10 Mbps/1 Mbps. January will be the time to let them know that we don’t want a slower Internet — we want an Internet for the future.
How Do I Do It?
Choose one day in January to take the challenge and on that day use ONLY your mobile device to access the Internet. During that day, share your experiences on social media using #MobileOnly. When your day is over, encourage your friends to also take the challenge. Don’t forget to contact @FCC during and after your challenge to let them know that mobile only is inadequate for Americans in the 21st century.
Get More Info, Spread The Word
Update 12/22/2017: Original maps generated on December 11th and used for these fact sheets understated the population of Americans forced to obtain services from known network neutrality violators. The problem is even greater than we originally calculated. We've update our maps and our fact sheets to reflect the more accurate data.
Network neutrality protects Americans from the ability of powerful ISPs to exercise unchecked power over what subscribers access and how quickly they receive certain content. The neutral characteristic of the Internet is one of its finest qualities. If Republican FCC Commissioners and Chairman Ajit Pai vote to shred network neutrality on December 14th as they’ve indicated, 177 million Americans will be left to the whims of a flawed market.
Mapping It Out, Presenting The Fact (Sheets)
We recently presented visualizations based on FCC Form 477 data that supports our findings on the way the repeal will limit vast swaths of people to a bleak Internet access future. Nationwide, approximately 29 million people have no broadband Internet access. Another 129 million will have no ability to change Internet access providers because there is no other option. Out of those folks, 48 million are forced to take service from an ISP that is a known network neutrality violator. Likewise, 146 million may have a choice between two ISPs, but about 52 million must choose between two network neutrality violators that have actively worked to undermine the policy for years.
Our team also parsed out the numbers for California and the East Coast from Maine to Virginia. The results are just as discouraging.
In our fact sheets, we focused on the number of people who either have no broadband access or who will be forced to take service from a firm that is a known violator of network neutrality. We've included our maps to help illustrate just how pervasive this problem is in each region.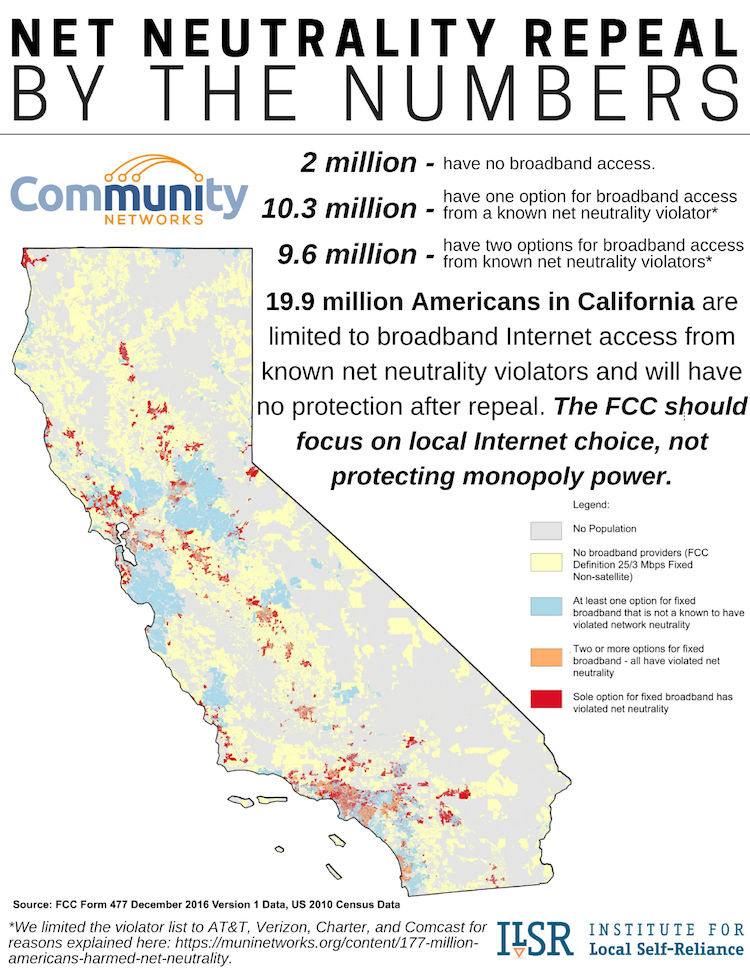
As the FCC’s vote on whether or not to remove network neutrality draws near, an increasing number of people are beginning to wonder how Internet access will change for them. Journalists have reached out to us to ask about the role of publicly owned Internet networks and the future without federal network neutrality policy protections. Molly Wood from Marketplace Tech interviewed Christopher to ask about the pros and cons of munis, how the FCC vote could affect municipal networks, and how municipal networks may help when or if we face an Internet no longer protected by network neutrality.
Wood asked some general questions about munis and their cost, and Christopher offered some specific examples from information we’ve learned from the communities we study. Now that big ISPs are set to receive the keys to the kingdom, local leaders wonder if they can take steps to avoid the pitfalls of unfettered power.
Christopher told Molly:
The only way that [ending network neutrality] would help cities and people more generally is that it would lead to more cities considering this and cities being more aggressive because the big cable and telephone companies would likely abuse their new power. But the Internet will still be there behind the scenes and cities can build their own apps and get around the barriers that the big cable and telephone companies are producing.
Listen here or at the Marketplace website.